The <h:commandLink> renders a link that acts like a submit button when clicked
Common/basic usage in JSF (I) - submit form, but don't invoke a method bean and navigate back to this page:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8' ?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0
Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:h="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/html">
<h:head>
<title>JSF commandLink examples</title>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<span>Name: #{playerBean.name} | E-mail:
#{playerBean.email}</span>
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"/>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
The <h:commandLink> will be rendered in HTML as:
<a onclick="mojarra.jsfcljs(document.getElementById('j_idt8'),{'j_idt8:j_idt13':'j_idt8:j_idt13'},'');return
false" href="#">Send</a>
The
PlayerBean will be:
package beans;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.enterprise.context.SessionScoped;
import javax.inject.Named;
@Named
@SessionScoped
public class PlayerBean implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String email;
// used in More Examples section
private String weburl;
private String countrycode;
private String age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
// more getters and setters - for weburl, countrycode
and age
}
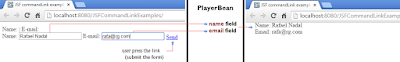
Data flow in image:
Common/basic usage in JSF (II) - submit form, invoke a method bean and navigate to this page:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8' ?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0
Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:h="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/html">
<h:head>
<title>JSF commandLink examples</title>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<span>Name: #{playerBean.name} | E-mail:
#{playerBean.email}</span>
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="#{playerBean.save()}"/>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
The <h:commandLink> will be rendered in HTML as (in Mojarra):
<a onclick="mojarra.jsfcljs(document.getElementById('j_idt15'),{'j_idt15:j_idt20':'j_idt15:j_idt20'},'');return
false" href="#">Send</a>
The
PlayerBean will be:
package beans;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.enterprise.context.SessionScoped;
import javax.inject.Named;
@Named
@SessionScoped
public class PlayerBean implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String email;
// used in More Examples section
private String weburl;
private String countrycode;
private String age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
// more getters and setters - for weburl, countrycode
and age
public void save()
{
System.out.println("Saving data [save()]
...");
}
}
Data flow in image:
Common/basic usage in JSF (III) - submit form, but don't invoke a method bean and navigate to data.xhtml page:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8' ?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0
Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:h="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/html">
<h:head>
<title>JSF commandLink examples</title>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<span>Name: #{playerBean.name} | E-mail:
#{playerBean.email}</span>
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="data"/>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
The
<h:commandLink>
will be rendered in HTML as:
<a onclick="mojarra.jsfcljs(document.getElementById('j_idt22'),{'j_idt22:j_idt27':'j_idt22:j_idt27'},'');return
false" href="#">Send</a>
The
PlayerBean will be:
package beans;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.enterprise.context.SessionScoped;
import javax.inject.Named;
@Named
@SessionScoped
public class PlayerBean implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String email;
// used in More Examples section
private String weburl;
private String countrycode;
private String age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
// more getters and setters - for weburl, countrycode
and age
}
And, the
data.xhtml is:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8' ?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0
Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:h="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/html">
<h:head>
<title></title>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<!-- View submitted data
-->
Name: <h:outputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/><br/>
Email: <h:outputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/><br/>
<!-- needed in More Examples section -->
Website URL: <h:outputText
value="#{playerBean.weburl}"/><br/>
Country code: <h:outputText
value="#{playerBean.countrycode}"/><br/>
Age: <h:outputText
value="#{playerBean.age}"/><br/>
</h:body>
</html>
Data flow in image:
More examples:
Submit form, but don't invoke a method bean and navigate to data.xhtml page with redirect (POST-GET-REDIRECT)
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="data?faces-redirect=true"/>
</h:form>
Note When you are
using redirect you need to know that data stored in request/view scoped are
lost and the browser address will reveal the page name (e.g. data.xhtml).
Submit form, invoke a
method bean and navigate to data.xhtml page from method
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="#{playerBean.saveAndGo()}"/>
</h:form>
The
saveAndGo() method will be:
public String saveAndGo()
{
System.out.println("Saving data [saveAndGo()]
...");
return "data";
}
Use style attribute to add custom
styles to a link
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="data" style="background-color:green;color:yellow;padding:4px;"/>
</h:form>
Use styleClass attribute to add custom
styles to a link
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="data" styleClass=" linkcss"/>
</h:form>
Disabled link (will
render a span element)
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="data" disabled="true"/>
</h:form>
Use of actionListener attribute
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
actionListener="#{playerBean.save}"/>
</h:form>
The save() method will be:
public void save(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("Saving data
[save(ActionEvent)] ...");
}
Note Do not use actionListener instead of action!
ActionListener
gets fired first, and it allows us to
modify the response, before Action gets called and perform the business logic
and find the next page location (same page or other page). Read more on Stack Overflow!
Use of actionListener and action attributes (I)
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
actionListener="#{playerBean.save}" action="data"/>
</h:form>
The save() method will be:
public void save(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("Saving data
[save(ActionEvent)] ...");
}
Note After the save()
method is invoked, the returned page
will be, data.xhtml.
Use of actionListener and action attributes (II)
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
actionListener="#{playerBean.save}"
action="#{playerBean.save()}"/>
</h:form>
The save() method invoked
via actionListener (first called)
is:
public void save(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("Saving data
[save(ActionEvent)] ...");
}
The save() method invoked
via action (second called) is:
public void save()
{
System.out.println("Saving data [save()]
...");
}
Use of <f:actionListener> tag
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send">
<f:actionListener
type="beans.PlayerActionListener"/>
</h:commandLink>
</h:form>
The
PlayerActionListener
class is:
package beans;
import javax.faces.event.AbortProcessingException;
import javax.faces.event.ActionEvent;
import javax.faces.event.ActionListener;
public class PlayerActionListener implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void
processAction(ActionEvent event) throws AbortProcessingException {
System.out.println("Player action listener
...");
}
}
Note When you are
using the <f:actionListener> the method name
must be processAction(), which comes from ActionListener interface. You
can choose the name of the method when you use
actionListener
attribute. Read more on StackOverflow!
Use of <f:actionListener> tag and actionListener, action attributes
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
actionListener="#{playerBean.save}"
action="#{playerBean.save()}">
<f:actionListener
type="beans.PlayerActionListener"/>
</h:commandLink>
</h:form>
The
save() method
invoked via actionListener (first called)
is:
public void save(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("Saving data
[save(ActionEvent)] ...");
}
The
processAction()
method invoked via <f:actionListener> (second called)
is:
public void processAction(ActionEvent event)
throws AbortProcessingException {
System.out.println("Player action listener
...");
}
The
save() method
invoked via action (third called) is:
public void save()
{
System.out.println("Saving data [save()]
...");
}
Use of <f:setPropertyActionListener> tag
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="data">
<f:setPropertyActionListener
target="#{playerBean.countrycode}" value="ro" />
<f:setPropertyActionListener
target="#{playerBean.weburl}"
value="http://www.rafaelnadal.com" />
</h:commandLink>
</h:form>
Note The <f:setPropertyActionListener> tag uses an
action listener (created by the framework) to directly set a value into a
managed bean property; it is placed within a component derived from the ActionSource class. The target
attribute indicates the managed bean
property, while the value attribute
indicates the value of the property.
Make a Cancel like link using immediate attribute (reset inputs
to empty strings)
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText value="#{playerBean.email}"
validator="myValidator"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="data"/>
<h:commandLink value="Reset"
immediate="true"
action="#{playerBean.resetWithImmediate()}"/>
</h:form>
<h:messages style="color:red;"/>
The
resetWithImmediate()
method is:
public String resetWithImmediate()
{
this.name = "";
this.email =
"";
return "index";
}
Pass extra parameters via <f:param> tag
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="#{playerBean.saveAndParam()}">
<f:param
name="playerCountryCode" value="RO"/>
<f:param
name="playerWeburl" value="http://www.rafaelnadal.com"/>
</h:commandLink>
</h:form>
The
saveAndParam()
method is:
public String saveAndParam() {
System.out.println("Saving data [saveAndParam()]
...");
FacesContext fc =
FacesContext.getCurrentInstance();
Map<String, String> params =
fc.getExternalContext().getRequestParameterMap();
this.countrycode =
params.get("playerCountryCode");
this.weburl =
params.get("playerWeburl");
return "data";
}
Assign the value of the
attribute named value of a <h:commandLink> tag via <f:attribute> tag
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink action="data">
<f:attribute name="value"
value="Send" />
</h:commandLink>
</h:form>
Pass extra parameters via <f:attribute> tag
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
actionListener="#{playerBean.saveAndAttributes}"
action="data">
<f:attribute
id="playerCountryCode" name="playerCountryCodeAttr"
value="RO"/>
<f:attribute
id="playerWeburl" name="playerWeburlAttr"
value="http://www.rafaelnadal.com"/>
</h:commandLink>
</h:form>
The
saveAndAttributes()
method is :
public void saveAndAttributes(ActionEvent e)
{
System.out.println("Saving data
[save(saveAndAttributes)] ...");
this.countrycode = (String)
e.getComponent().getAttributes().get("playerCountryCodeAttr");
this.weburl = (String)
e.getComponent().getAttributes().get("playerWeburlAttr");
}
Include view parameters
in redirect
<h:head>
<f:metadata>
<f:viewParam name="ccp"
value="#{playerBean.countrycode}"/>
<f:viewParam name="wup"
value="#{playerBean.weburl}"/>
</f:metadata>
</h:head>
<h:form>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Submit"
action="data?faces-redirect=true&includeViewParams=true"/>
</h:form>
Simple AJAX submit
<h:form>
<span>Name: #{playerBean.name} | E-mail:
#{playerBean.email}</span><br/>
Name: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="#{playerBean.save()}">
<f:ajax execute="@form"
render="@form"/>
</h:commandLink>
</h:form>
The save() method is:
public void save()
{
System.out.println("Saving data [save()]
...");
}
Simple AJAX partial
submit (only the player name and e-mail will be submitted)
<h:form>
<span>Name: #{playerBean.name} | E-mail:
#{playerBean.email} | Age: #{playerBean.age}</span><br/>
Name: <h:inputText id="nameId"
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText id="emailId"
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
Age: <h:inputText id="ageId"
value="#{playerBean.age}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="#{playerBean.save()}">
<f:ajax execute="nameId
emailId" render="@form"/>
</h:commandLink>
</h:form>
The
save() method
is:
public void save()
{
System.out.println("Saving data [save()]
...");
}
Simple Cancel AJAX link
<h:form>
<span>Name: #{playerBean.name} | E-mail:
#{playerBean.email} | Age: #{playerBean.age}</span><br/>
Name: <h:inputText id="nameId"
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText id="emailId"
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
Age: <h:inputText id="ageId"
value="#{playerBean.age}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="#{playerBean.save()}">
<f:ajax execute="@form"
render="@form"/>
</h:commandLink>
<h:commandLink value="Cancel">
<f:ajax
execute="@this" render="@form"/>
</h:commandLink>
</h:form>
The save() method is:
public void save()
{
System.out.println("Saving data [save()]
...");
}
The Cancel AJAX link with reset to a
set of default values (empty strings)
<h:form>
<span>Name: #{playerBean.name} | E-mail:
#{playerBean.email} | Age: #{playerBean.age}</span><br/>
Name: <h:inputText id="nameId"
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
E-mail: <h:inputText id="emailId"
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
Age: <h:inputText id="ageId"
value="#{playerBean.age}"/>
<h:commandLink value="Send"
action="#{playerBean.save()}">
<f:ajax execute="@form"
render="@form"/>
</h:commandLink>
<h:commandLink value="Cancel"
action="#{playerBean.reset()}">
<f:ajax execute="@this"
render="@form"/>
</h:commandLink>
</h:form>
The save() method is:
public void save()
{
System.out.println("Saving data [save()]
...");
}
The reset() method is:
public void reset()
{
this.name = "";
this.email = "";
this.age = "";
}
Submit form via
JavaScript (the JSF link is not visible)
<input type="button"
value="Fake Command" onclick="clickJSFLink();"/>
<h:form id="myFormId">
<h:inputHidden id="nameHiddenId"
value="#{playerBean.name}"/>
<h:inputHidden id="emailHiddenId"
value="#{playerBean.email}"/>
<h:commandLink id="btnId"
value="Send" action="data" style="display:none;"/>
<script type="text/javascript">
function clickJSFLink() {
document.getElementById("myFormId:nameHiddenId").value = "Rafael
Nadal";
document.getElementById("myFormId:emailHiddenId").value =
"rafa@rg.com";
if (confirm('Are you sure you want to submit the JSF
form ?')) {
document.getElementById("myFormId:btnId").click();
}
}
</script>
Complete source code on GitHub.
See also Mkyong.com.
More resources on Constantin Alin, ZEEF page.
CommandLink in JSF Extension on JSF ShowCase ZEEF page.
See also Mkyong.com.
More resources on Constantin Alin, ZEEF page.
CommandLink in JSF Extension on JSF ShowCase ZEEF page.











 Arrays
Arrays Converters
Converters


 JSF 2 Tutorials at www.mkyong.com
JSF 2 Tutorials at www.mkyong.com  JavaServer Faces (JSF) Tutorial
JavaServer Faces (JSF) Tutorial 





















Niciun comentariu :
Trimiteți un comentariu